The significance of health information exchange (HIE) in healthcare cannot be overstated. It serves as the lifeline of modern healthcare systems, ensuring the right information is available at the right time, to the right people. This seamless flow of patient data not only enhances the quality of care but also optimizes healthcare delivery processes, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
One of the most profound impacts of efficient exchange of health information is on patient safety. By having real-time access to patient health records, healthcare providers can make informed decisions, avoid duplicate tests and procedures, and reduce the likelihood of medical errors. This level of coordination and collaboration among providers, facilitated by HIE, is essential for offering comprehensive, effective and efficient patient care.
Furthermore, health information exchange plays a critical role in public health and research. It enables the aggregation and analysis of health data across populations, providing valuable insights into disease patterns, treatment outcomes, and healthcare disparities. This collective knowledge is instrumental in shaping public health policies, advancing medical research, and ultimately, improving community health. As the public health sector gains access to these data, social determinants of health (which are defined as the conditions in the environment where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age) can be addressed more effectively and improve population health outcomes.
Creating a Framework
The Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement (TEFCA), represents a significant leap forward in the standardization and nationwide scaling of health information exchange. Developed by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC HIT), TEFCA aims to establish a universal set of principles, terms, and conditions to support the seamless and secure exchange of health information across disparate networks.
At its core, TEFCA is designed to foster trust among participating entities. By adhering to a common set of rules and technical standards, organizations can confidently exchange health data, knowing that their counterparts are committed to the same level of security, privacy, and interoperability.
The implementation of TEFCA also addresses one of the longstanding challenges in health information exchange: interoperability. With multiple health information networks operating on different standards and protocols, the exchange of data has often been fragmented and inefficient. TEFCA paves the way for a more unified approach, where networks can connect and communicate seamlessly, breaking down barriers to information flow and enhancing the continuity of care. Healthcare organizations can connect to a broader network of providers and access a more comprehensive view of patient health information, facilitating better-informed clinical decisions and more coordinated care.
Creating the Network
Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs) are at the heart of TEFCA’s vision for a unified health information exchange landscape. The first QHINs were established and opened for initial limited data exchange in late December of 2023. As entities certified by the ONC, QHINs will serve as the backbone for cross-network health information exchange, facilitating the secure and efficient transfer of health data among a wide array of healthcare stakeholders, including providers, payers, and public health agencies.
The role of QHINs extends beyond mere data conduits. They are instrumental in enforcing the common rules and standards set forth by TEFCA, ensuring all participants adhere to the agreed-upon protocols for data exchange. This includes the implementation of robust security measures, the protection of patient privacy, and the promotion of data interoperability across different health IT systems.
QHINs will act as central hubs, through the implementation of common technical standards and protocols, enabling the transfer of data across networks, regardless of the underlying technology. This will not only simplify the process of connecting to new partners but also reduce the technical barriers to interoperability.
FHIR, or Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, developed by Health Level Seven International (HL7), is a standard describing data formats and elements, known as resources, and an application programming interface (API) for exchanging electronic health records. The strength of FHIR lies in its open-access, flexibility and ease of implementation, making it the TEFCA-recommended framework for developing interoperable healthcare applications.
e-Prescribing and Medication Management
The National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP) is another key organization involved in promoting interoperability within the healthcare industry. They focus specifically on standardizing electronic prescribing and medication-related transactions. By establishing consistent formats and protocols for transmitting prescription data, the NCPDP plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and secure medication management across different healthcare systems. Their efforts contribute to…
- Reducing medication errors
- Improving patient safety
- Streamlining the prescription fulfillment process
The mission and vision of the NCPDP is to advance patient safety and healthcare efficiency through the development and implementation of industry-wide standards for electronic prescribing and medication-related transactions.
The secure exchange of prescription data enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and deliver optimal care to their patients. With a focus on reducing medication errors and improving patient outcomes, the NCPDP plays a vital role in promoting interoperability and enhancing the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
Structured and Codified Sig Format Implementation Guide Version 2.2 COPYRIGHT (©) National Council for Prescription Drug Programs, Inc. 2019
A prescription contains a number of different elements. In addition to the patient and prescriber information, it must state the name, dosage form and strength of the medication; the dose; the amount to be dispensed; the number of refills; and the directions for use, or Sig. The Sig contains the instructions explaining how the patient is to take the medication. It must be legible, unambiguous, and complete to ensure the prescriber’s instructions for use of the product are understood.
How RxLive is improving medication management
Since our beginning, RxLive’s vision has been to improve healthcare by leveraging the value of clinical pharmacists. The way we execute on that is by leaning into our commitment to clarity. Using the technical standards that are available to support the clear and accurate exchange of medication-related data is one way we ensure our platform and services support our mission of delivering meaningful interactions between patients, pharmacists and healthcare providers through cutting-edge technology and clinical guidance.
We partnered with the NCPDP to use their Structured and Codified Sig (instructions for use, from the Latin ‘signatura’) Format Standard to develop and train a large language model (LLM) to convert free-text medication directions for use into the codified standard. The intent was to facilitate communication between prescribers and pharmacists, help reduce the opportunity for errors, and track provider action following a clinical pharmacist’s medication recommendation.
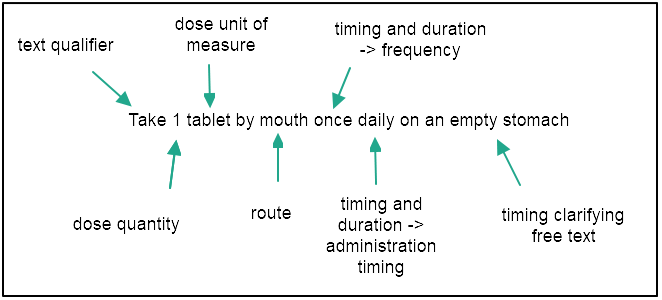
Ultimately, the hope is that by standardizing the medication directions for use and sharing that information back as a part of the patient’s active medication list, fewer preventable medication errors will occur and accurate medication histories can be shared between patients and their healthcare providers.
Let’s Connect!
Interested in learning more about how RxLive can help you recommit to your patients and your value-based care approach? Get in touch or sign up for our newsletter.


